18 results
Physical science Common Core 5.MD.B.2 resources

Scientific Method Lab: Paper Airplane Model Design
This “Scientific Method Lab: Paper Airplane Design" was designed for my 5th grade class, but it can easily be used with any grade level. The Big Idea would be force and motion.Older students might even like to “tweak” the lab and design their own paper airplane models!Included are lab instructions following the scientific method, a data recording sheet, and the paper airplane foldables. The lab follows the scientific method, but it does not include a Review of Literature, an abstract, or a disp
Subjects:
Grades:
4th - 6th
Types:
Also included in: Scientific Method Bundle

Monthly Weather Graph Charting ***BUNDLE***
This bundle includes weather graphs for September through June! Teach kids to graph using daily weather with these fun weather graphs! Graphics are tapered to monthly themes, they are great for grades K-5.
Subjects:
Grades:
K - 5th

On Track and Up to Speed - Forces and Motion 25-Activity Booklet
On Track and Up to Speed - Forces and Motion 25-Activity BookletThese 25 activities use the science and math behind the popular sport of Auto Racing to investigate and understand forces and motion.
Grades:
5th - 12th
Types:
NGSS:
MS-PS2-4
, MS-PS2-2
, HS-PS2-1
, 5-PS2-1
, 3-5-ETS1-2
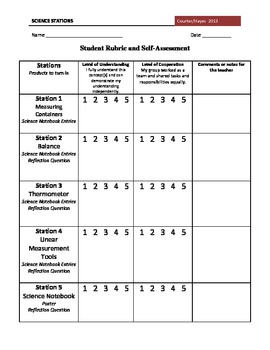
One Stop Shop Science Stations- Science Tools
Lesson Plans are based on the Constructivist Theory (students construct their own understanding of the world through hands-on experiences and reflecting. The teacher serves as a facilitator and creates new understandings through coaching, moderating, suggesting and questioning. These lessons will enable students to:
• be active participants in the learning process
• construct knowledge from experience
• learn through personal interpretation of the world
• problem solve
• use authentic tasks, ex
Subjects:
Grades:
3rd - 6th
Types:

Graphing without Numbers - STEM
Title: Graphing Without Numbers: LUNAR STATION Theme / Topic: Graphs & Coordinate PlanesEssential Question: What do the marks on a graph represent? How can I use data to make decisions?Recommended Level: K-5Purpose: To introduce the concept of data-driven decision-making through graphs and charts.
Subjects:
Grades:
K - 5th
Types:
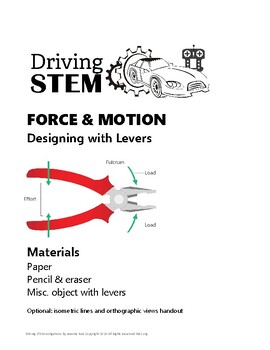
FORCE & MOTION Designing with Levers - 7th Grade DRIVING STEM
ACTIVITY: DIAGRAMMING LEVERSPurpose: Diagram a household machine. Extend knowledge by designing, diagramming, and recreating simple machines.View several diagrams of working machines from this lesson. Examine features of diagrams including labels and point-of-view. In this STEMvestigation, you will investigate levers, then draw and label sketches to indicate motion, direction of motion, and other information that might be useful in recreating the machine.ESSENTIAL QUESTIONSWhat is the function o
Grades:
5th - 8th
Types:
NGSS:
3-5-ETS1-3
, 3-5-ETS1-1
, MS-PS2-2
, 5-PS2-1
, 3-5-ETS1-2
...

Drop Zone: Parachute Design Project-Based Learning Lab
This highly adaptable investigation will engage students of many ages and levels. Options for primary, upper elementary, and middle school are included. This is a true STEM lab that incorporates the science, technology engineering, and math components. Common, inexpensive, and easily available materials make this an easy lab to teach yet it produces maximum learning and engagement in your classroom. NGSS and Common Core Math Standards alignment are included in this "STEM on a Shoestring Budget"
Subjects:
Grades:
1st - 8th
Types:

Logbooks Are Lifelines
MATERIALS3-ring binder & paper or spiral bound notebookglue stick or tapepen and pencilOPTIONAL: digital camera, colored pencils & highlighters
Grades:
5th - 8th
Types:
NGSS:
3-5-ETS1-3
, 3-5-ETS1-1
, MS-PS2-2
, 5-PS2-1
, 3-5-ETS1-2
...

Newton's 2nd Law of Motion Activity f=ma: Crash Barriers Lesson & Demonstration
How Does Force Relate to Mass? Crash Barriers. ENGAGE Place a 2-3 meter long strip of tape on the floor to form a “track.” At the end of the track, place a solid object (a heavy book or piece of wood) that will stop the car in a simulated crash...EXPLOREBrainstorm ideas for creating a safer “crash barrier”, one that absorbs some of the energy of a crash. Make a plan. Describe the barrier your group will create......Test the barriers to determine which one most effectively changes the amount of e
Grades:
5th - 9th
Types:
NGSS:
MS-PS2-4
, MS-PS2-2
, HS-PS2-1
, 5-PS2-1
, 3-5-ETS1-2
...
Also included in: Newton's Laws Bundle

STEM Forces & Motion (3rd-5th) grade Energy Bounce DRIVING STEM
ENERGY BOUNCEStudents are challenged to investigate potential and kinetic energy as they look for patterns in the way a ball bounces. Collect data. Analyze data. Make decisions using data. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS1. What is the difference in kinetic and potential energy?2. What are some examples of energy transversions?Potential energy is energy that is stored in an object. If you stretch a rubber band, you will give it potential energy. As the rubber band is released, potential energy is changed to
Grades:
2nd - 5th
Types:
NGSS:
K-2-ETS1-2
, K-2-ETS1-3
, K-2-ETS1-1
, 3-5-ETS1-3
, 4-PS3-3
...

DRIVING STEM Pendulum Swing - Forces & Motion, Time, and Gravity
Motion, Time, and Gravity: Investigate the pendulum, periodic motion, elapsed time, and load/mass/weight. Read "What Is a Second" before discussion and introduction of the challenge. Students will investigate length, load, and materials in order to design a pendulum constant and predictable motion. Essential Question: What determines the period of a pendulum? Recommended Level: 5-8 Time: Approximately 50 minutesPurpose: Introduce the concept of periodic motion. Students discover that the period
Grades:
5th - 8th
Types:
NGSS:
MS-ETS1-2
, 3-5-ETS1-3
, MS-ETS1-4
, 3-5-ETS1-1
, MS-PS2-2
...

Going Bananas With Measuring
Let's go bananas with measuring length and mass using standard and non-standard units. Bananas are easy to purchase and make excellent objects to measure and compare. Reading selections provide background information about bananas. Follow up question pages are differentiated for two levels of learners. Experiments range from easy counting to using calculators to find averages and percent. Compare mass of banana with other objects on balance scales, use non-standard units to determine length
Grades:
1st - 5th
Types:
NGSS:
K-2-ETS1-3

Poster: Basic Math Skills for Chemistry or Science (12 x 39) - No QR codes
Are students having trouble with the mathematics involved with Chemistry, Physics, or other science courses?Many students have shown up to my class lacking basic math skills that are required for science courses (multiplication, division, fractions, scientific notation, significance, etc.). This poster can hang in the room and hopefully be a reminder of those skills. The poster also makes and effort to address the mnemonic device/ shortcut of the teacher dreaded triangle math for things like d
Subjects:
Grades:
5th - 12th, Higher Education
Types:

STEM Simple Machines Forces & Work 5th-8th Grade DRIVING STEM
SIMPLE MACHINESCan you find examples of these simple machines on a very complex machine? Levers, Inclined Plane, Wedge, Screw thread, Wheel; Wheel and axel, Pulley. Collect data. Analyze data. Make decisions using data. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONSWhat is the function of this machine?How many moving parts does it have?How are the moving parts connected to each other?What does each moving part do in the machine?Which parts are elements of machines?A machine is a tool used to make work easier. Simple mach
Grades:
5th - 8th
Types:
NGSS:
3-5-ETS1-3
, 3-5-ETS1-1
, MS-PS2-2
, 5-PS2-1
, 3-5-ETS1-2
...
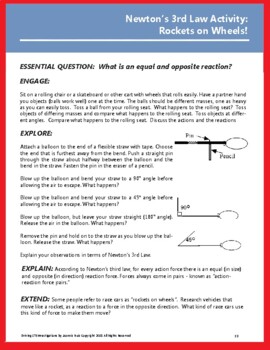
Newton's 3rd Law Activity: Action-Reaction Force Pairs Demonstration
What Is an Equal and Opposite Reaction? ENGAGE Sit on a rolling chair or a skateboard or other cart with wheels that rolls easily. Have a partner hand out objects (balls work well) one at the time. The balls should be different masses, one as heavy as you can easily toss. Toss a ball from your rolling seat...EXPLOREAttach a balloon to the end of a flexible straw with tape. Choose the end that is furthest away from the bend. Push a straight pin through the straw about halfway between the balloon
Grades:
5th - 9th
Types:
NGSS:
MS-PS2-4
, MS-PS2-2
, HS-PS2-1
, 5-PS2-1
, 3-5-ETS1-2
...
Also included in: Newton's Laws Bundle
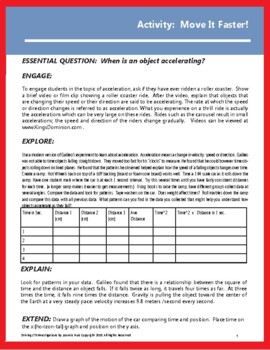
Acceleration Activity: Galileo's Inclined Plane - Lessons, Demonstrations & Data
WHEN IS AN OBJECT ACCELERATING? ENGAGE To engage students in the topic of acceleration, ask if they have ever ridden a roller coaster. Show a brief video or film clip showing a roller coaster ride. After the video, explain that objects that are changing their speed or their direction are said to be accelerating. The rate at which the speed or direction changes is referred to as acceleration...EXPLOREUse a modern version of Galileo’s experiment to learn about acceleration. Acceleration means a
Grades:
5th - 12th
Types:
NGSS:
MS-PS2-4
, MS-PS2-2
, HS-PS2-1
, 5-PS2-1
, 3-5-ETS1-2
Also included in: Newton's Laws Bundle

STEM Forces & Motion (6th, 7th, 8th) Energy Bounce DRIVING STEM
ENERGY BOUNCEStudents are challenged to investigate potential and kinetic energy as they look for patterns in the way a ball bounces. Collect data. Analyze data. Make decisions using data. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS1. What is the difference in kinetic and potential energy?2. What are some examples of energy transversions?Potential energy is energy that is stored in an object. If you stretch a rubber band, you will give it potential energy. As the rubber band is released, potential energy is changed to
Grades:
6th - 8th
Types:
NGSS:
K-2-ETS1-2
, K-2-ETS1-3
, K-2-ETS1-1
, 3-5-ETS1-3
, MS-PS2-4
...

Newton's Laws: 1st Law of Inertia, Forces & Motion-Lab, Lessons & Demonstrations
WHEN IS INERTIA? ENGAGE Place a half-filled cup of water on a rolling cart. Have students observe as you give the cart a good push, ie., force. Position the cart so that it will hit a solid surface like a wall. Initially, the cup and water will slide back (choosing to stay in place) demonstrating the first part of the law of inertia. Then the water moves in the same direction as the cart and the cup keeps moving as well. This demonstrates that the static friction of the cart on the cup overcome
Grades:
5th - 8th
Types:
NGSS:
MS-PS2-4
, MS-PS2-2
, 5-PS2-1
, 3-5-ETS1-2
, MS-PS2-1
Also included in: Newton's Laws Bundle
Showing 1-18 of 18 results





