Long Division Task Cards: The Box or Area Method
- PDF
What educators are saying
Also included in
- Are you working on multi-digit division in your classroom? This is one of the most challenging concepts that we face as teachers. Luckily, there are several very effective strategies for teaching this concept! This is a bundle of nine sets of long division task cards. Each set of task cards providesPrice $20.97Original Price $29.50Save $8.53
- This is a discounted bundle of long division resources.Please view the bundle contents to see exactly what is included.Price $36.99Original Price $47.49Save $10.50
Description
These task cards are also included in a Long Division Big Bundle. This includes nine sets of task cards for a variety of Long Division alternatives and strategies. See it HERE.
Are you looking for even more support with teaching long division in your classroom? You might be interested in this self-paced, student-centered Long Division Station that will allow your students to move through all of these strategies and approaches at their own pace. That station can be found HERE.
***********************************************************************
Are you working on multi-digit division in your classroom? This is one of the most challenging concepts that we face as teachers. Luckily, there are several very effective strategies for teaching this concept!
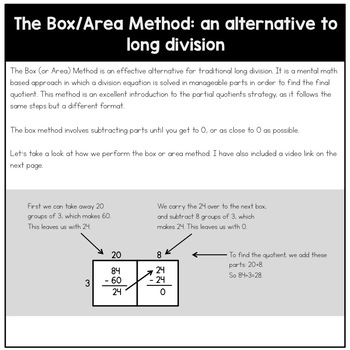
The box method - also known as the area method - is an effective alternative for traditional long division. It is a mental math based approach in which a division equation is solved in manageable parts in order to find the final quotient.
The box method involves multiplying and then subtracting parts until you get to 0, or as close to 0 as possible. If you cannot get down to 0, then there is a remainder.
This is a fantastic way to lead students into the partial quotients strategy - a "must-teach" alternative for long division.
This resource is a fantastic supplement to those teachers currently using the Long Division Station in their classroom. It can be used as extra practice for the Box Method level when students get to that point in the station.
This resource includes:
- detailed explanations and examples of the box method for division
- a link to a video explaining the box method
- a box method strategy poster to hang in the classroom for easy reference
- 24 task cards that will have students practicing the box method in a variety of different ways to enhance understanding
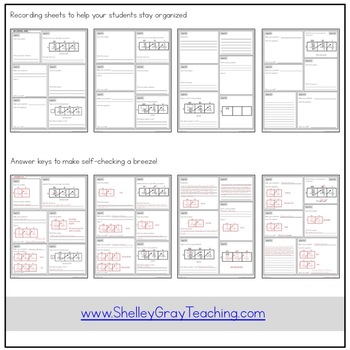
- recording sheets to keep students organized
- answer keys to make self-checking a breeze
You may also be interested in: