Data Distribution positive/negative skewed fillable notes UPDATED
Math be Mathing
10 Followers
Grade Levels
6th - 12th, Higher Education, Adult Education, Homeschool
Subjects
Resource Type
Standards
CCSSHSS-ID.A.1
CCSSHSS-ID.A.2
CCSSHSS-ID.A.3
CCSSHSS-ID.A.4
CCSSHSS-ID.B.5
Formats Included
- Google Docs™
Pages
4 pages
Math be Mathing
10 Followers

Made for Google Drive™
This resource can be used by students on Google Drive or Google Classroom. To access this resource, you’ll need to allow TPT to add it to your Google Drive. See our FAQ and Privacy Policy for more information.
Also included in
- Unit 9: Data and Stats(No 9.3/ Skip)9.1 Central Tendencies: Mean, Median and Mode9.2 Graphical Data: Bar Charts, Dot Plots and Histograms9.3 NONE9.4A 5 number summary and box and whisker plots 9.4B Standard Deviation9.5/9.6 Data Distributions (skewness) left or right9.7 Frequency Tables and relativePrice $11.50Original Price $11.70Save $0.20
Description
Unit 9: Data and Stats: Updated
(No 9.3/ Skip)
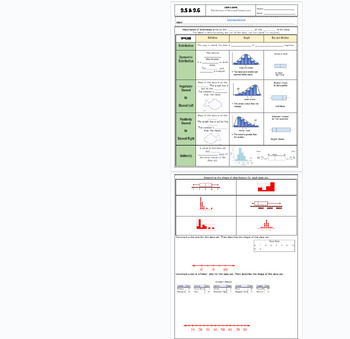
9.5/9.6 Data Distribution (skewness)
Students go over the vocabulary and complete the examples with the vocabulary scaffolded. Skewness is explained and how to identify it comparing data charts and box and whisker plots. Uses many visuals and examples to differentiate between that different graphs. Notes are scaffolded. Includes hook video hyperlinked on the "learning objective" title. Key is included and hyperlinked as a PDF in the heading highlighted in the orange box, and at the bottom of the google doc as well. Google doc is editable, used in M1 HS
Total Pages
4 pages
Answer Key
Included
Teaching Duration
1 hour
Report this resource to TPT
Reported resources will be reviewed by our team. Report this resource to let us know if this resource violates TPT’s content guidelines.
Standards
to see state-specific standards (only available in the US).
CCSSHSS-ID.A.1
Represent data with plots on the real number line (dot plots, histograms, and box plots).
CCSSHSS-ID.A.2
Use statistics appropriate to the shape of the data distribution to compare center (median, mean) and spread (interquartile range, standard deviation) of two or more different data sets.
CCSSHSS-ID.A.3
Interpret differences in shape, center, and spread in the context of the data sets, accounting for possible effects of extreme data points (outliers).
CCSSHSS-ID.A.4
Use the mean and standard deviation of a data set to fit it to a normal distribution and to estimate population percentages. Recognize that there are data sets for which such a procedure is not appropriate. Use calculators, spreadsheets, and tables to estimate areas under the normal curve.
CCSSHSS-ID.B.5
Summarize categorical data for two categories in two-way frequency tables. Interpret relative frequencies in the context of the data (including joint, marginal, and conditional relative frequencies). Recognize possible associations and trends in the data.