Work Smarter
63 Followers
Resource Type
Standards
CCSSHSN-RN.B.3
CCSSMP7
CCSSMP8
Formats Included
- PDF
Pages
8 pages
Work Smarter
63 Followers
Description
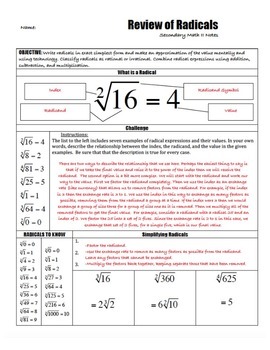
These notes (Teacher and Student versions) are an great way to prepare Math 2 students for N.RN.1 by teaching them to evaluate, estimate, add, subtract, and multiply radical expressions in every index. This lesson uses the patterns in radical expressions to help students create their own definitions and explanations for simplification processes. It also ties back into N.RN.3 requirements by showing students how to identify if radical expressions are rational or irrational.
These notes also work well as a review for Math 3 students.
These notes also work well as a review for Math 3 students.
Total Pages
8 pages
Answer Key
Included
Teaching Duration
2 days
Last updated Aug 29th, 2015
Report this resource to TPT
Reported resources will be reviewed by our team. Report this resource to let us know if this resource violates TPT’s content guidelines.
Standards
to see state-specific standards (only available in the US).
CCSSHSN-RN.B.3
Explain why the sum or product of two rational numbers is rational; that the sum of a rational number and an irrational number is irrational; and that the product of a nonzero rational number and an irrational number is irrational.
CCSSMP7
Look for and make use of structure. Mathematically proficient students look closely to discern a pattern or structure. Young students, for example, might notice that three and seven more is the same amount as seven and three more, or they may sort a collection of shapes according to how many sides the shapes have. Later, students will see 7 × 8 equals the well remembered 7 × 5 + 7 × 3, in preparation for learning about the distributive property. In the expression 𝑥² + 9𝑥 + 14, older students can see the 14 as 2 × 7 and the 9 as 2 + 7. They recognize the significance of an existing line in a geometric figure and can use the strategy of drawing an auxiliary line for solving problems. They also can step back for an overview and shift perspective. They can see complicated things, such as some algebraic expressions, as single objects or as being composed of several objects. For example, they can see 5 – 3(𝑥 – 𝑦)² as 5 minus a positive number times a square and use that to realize that its value cannot be more than 5 for any real numbers 𝑥 and 𝑦.
CCSSMP8
Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Mathematically proficient students notice if calculations are repeated, and look both for general methods and for shortcuts. Upper elementary students might notice when dividing 25 by 11 that they are repeating the same calculations over and over again, and conclude they have a repeating decimal. By paying attention to the calculation of slope as they repeatedly check whether points are on the line through (1, 2) with slope 3, middle school students might abstract the equation (𝑦 – 2)/(𝑥 – 1) = 3. Noticing the regularity in the way terms cancel when expanding (𝑥 – 1)(𝑥 + 1), (𝑥 – 1)(𝑥² + 𝑥 + 1), and (𝑥 – 1)(𝑥³ + 𝑥² + 𝑥 + 1) might lead them to the general formula for the sum of a geometric series. As they work to solve a problem, mathematically proficient students maintain oversight of the process, while attending to the details. They continually evaluate the reasonableness of their intermediate results.