Polynomials | Classification Standard Form Degree Leading Coefficient
Christine Laymon
51 Followers
Resource Type
Standards
CCSS7.EE.A.1
CCSSHSA-SSE.A.1a
CCSSHSA-APR.A.1
CCSSMP6
CCSSMP7
Formats Included
- PDF
- Internet Activities
- Easel Activity
- Easel Assessment
Pages
21 pages
Christine Laymon
51 Followers
Easel Activity Included
This resource includes a ready-to-use interactive activity students can complete on any device. Easel by TPT is free to use! Learn more.
Compatible with Digital Devices
The Teacher-Author has indicated that this resource can be used for device-based learning.
Easel Assessment Included
This resource includes a self-grading quiz students can complete on any device. Easel by TPT is free to use! Learn more.
What educators are saying
My students were engaged and were able to complete the assignment. It is a good resource for introducing polynomials and polynomial vocabulary. I will definitely use this resource again!
Description
This is a crash course on the language we use surrounding polynomials! This resource contains notes, a student worksheet, AND a Formative Assessment specially designed for EASEL by TPT.
- The 1st page is entirely notes on polynomials (split into monomials, binomials, and trinomials), includes examples and non-examples, labeled diagrams, and Language Connections.
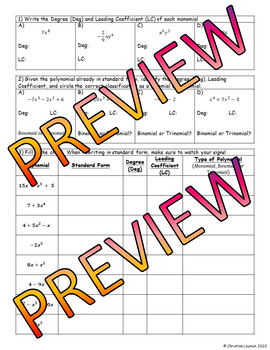
- The 2nd page contains student questions organized in a tabular format.
- Identifying degree and leading coefficient of monomials
- Identifying degree, leading coefficient, and classifying polynomials as either binomial or trinomial
- Given a polynomial, rewrite it in standard form as needed and then identify the degree, leading coefficient, and classify as monomial, binomial, or trinomial.
Contents:
- 2 Student Pages (non-editable PDFs) (notes are the first page). (enabled for EASEL by TPT as of 7/13/22)
- 1 Teacher Details/Contents Page
- 1 Teacher Tips Page
- 1 teacher answer key pages
- BONUS: 1 Formative Assessment specifically designed for EASEL by TPT.
- Multiple Choice (10 Questions - 1 per slide)
- Select all that apply (2 Questions - 1 per slide)
- Likert Scale Polls for student feedback (4 Questions - 1 per slide)
Related Products:
- Check out "Special Polynomial Patterns | Products and Factors | Fill In the Blank"
- Check out "Greatest Common Factor GCF Integer Circuit" for a GCF activity usable with 6th grade- Alg 1.
- Do your students struggle with Domain and Range? Check out "Domain Range and Function Stamp Rally"
- Check out "Synthetic Division & Intro to Rational Functions - Digital Drag & Drop".
- Check out "Multiplying Polynomials | Distribution FOIL Box Method Area Model"
- Looking for more Alg 1 or Alg 2 resources? Check out what I have to offer!
---------------------------------------------------------------------
⭐ Earn TPT Credits! ⭐
- After you have used the resource (at least 24 hours after purchase), earn TPT Credits by going to My Purchases and then leaving Feedback/Reviews on the resource! More info can be found in TPT's FAQ here.
- Feedback on free resources is appreciated too but will not earn you credits.
Connect with me!
Questions? You can use the TPT Q&A feature for this product or email me at ChristineLaymon123@gmail.com
©2022-2024 Christine Laymon
Please note - this resource is for use by the purchasing teacher only.
Electronic distribution is limited to the purchaser's classes only. Please use this resource in the spirit that it is intended.
Total Pages
21 pages
Answer Key
Included
Teaching Duration
1 hour
Report this resource to TPT
Reported resources will be reviewed by our team. Report this resource to let us know if this resource violates TPT’s content guidelines.
Standards
to see state-specific standards (only available in the US).
CCSS7.EE.A.1
Apply properties of operations as strategies to add, subtract, factor, and expand linear expressions with rational coefficients.
CCSSHSA-SSE.A.1a
Interpret parts of an expression, such as terms, factors, and coefficients.
CCSSHSA-APR.A.1
Understand that polynomials form a system analogous to the integers, namely, they are closed under the operations of addition, subtraction, and multiplication; add, subtract, and multiply polynomials.
CCSSMP6
Attend to precision. Mathematically proficient students try to communicate precisely to others. They try to use clear definitions in discussion with others and in their own reasoning. They state the meaning of the symbols they choose, including using the equal sign consistently and appropriately. They are careful about specifying units of measure, and labeling axes to clarify the correspondence with quantities in a problem. They calculate accurately and efficiently, express numerical answers with a degree of precision appropriate for the problem context. In the elementary grades, students give carefully formulated explanations to each other. By the time they reach high school they have learned to examine claims and make explicit use of definitions.
CCSSMP7
Look for and make use of structure. Mathematically proficient students look closely to discern a pattern or structure. Young students, for example, might notice that three and seven more is the same amount as seven and three more, or they may sort a collection of shapes according to how many sides the shapes have. Later, students will see 7 × 8 equals the well remembered 7 × 5 + 7 × 3, in preparation for learning about the distributive property. In the expression 𝑥² + 9𝑥 + 14, older students can see the 14 as 2 × 7 and the 9 as 2 + 7. They recognize the significance of an existing line in a geometric figure and can use the strategy of drawing an auxiliary line for solving problems. They also can step back for an overview and shift perspective. They can see complicated things, such as some algebraic expressions, as single objects or as being composed of several objects. For example, they can see 5 – 3(𝑥 – 𝑦)² as 5 minus a positive number times a square and use that to realize that its value cannot be more than 5 for any real numbers 𝑥 and 𝑦.