PHANTOM Rocket - Build a flying Model Rocket & Parachute w/ basic materials! PBL
Description
Check out this product review from a very satisfied (and amazing =) physics teacher:
Rated 5 out of 5
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐Extremely satisfied
"I used this resource in my high school physical science class. We LOVED this project! The project took us about 6 days to complete, but I think my future classes could get it done in 4 days now that I know how to run the project more smoothly. I highly recommend this project for any physical science teacher (or any class like it) as an end of the year project because I was able to relate every single topic that we covered back to the rocket!"
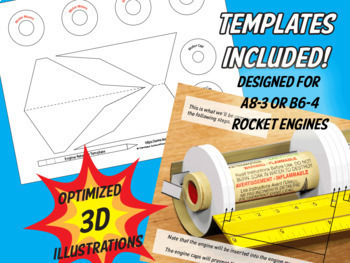
This is one of the most exciting STEM projects we have to offer with 60+ pages of large, clear & detailed illustrations.
Use household tools & materials to build a model rocket, complete with parachute recovery system.
The PHANTOM rocket is designed for use with an A8-3 or B6-0 rocket engine.
This product includes:
- Build manual in 3 formats that is optimized for:
+ Booklet printing
+ Viewing on a device
+ Viewing on a projector
- Plans & templates required to build the different rocket components.
Don't skip this project! Take advantage of the opportunity and give your students the unforgettable experience of launching a real, flying model rocket!