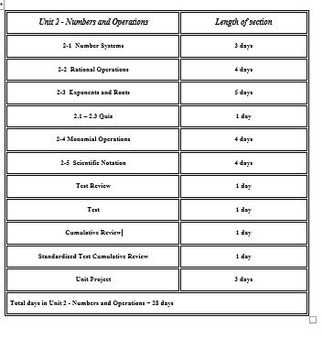
Number System: 8th Grade CCSS Numbers and Operations Unit
Better Way Math
63 Followers
Resource Type
Standards
CCSS8.SP.A.4
CCSS8.NS.A.1
CCSS8.NS.A.2
Formats Included
- Zip
Pages
56 pages, 23 powerpoints
Better Way Math
63 Followers
Description
These materials include a complete student and teacher manual that cover all of the CCSS for 8th grade Number System plus the Statistics and Probability Standard on Two-Way Tables. These materials include multiple day lessons for each topic. Powerpoint presentations accompany all of the multiple day lessons. These materials also include assessments. These materials will provide you with complete lessons that will engage your students. You will have zero prep time while using these materials.
Total Pages
56 pages, 23 powerpoints
Answer Key
Included
Teaching Duration
1 month
Report this resource to TPT
Reported resources will be reviewed by our team. Report this resource to let us know if this resource violates TPT’s content guidelines.
Standards
to see state-specific standards (only available in the US).
CCSS8.SP.A.4
Understand that patterns of association can also be seen in bivariate categorical data by displaying frequencies and relative frequencies in a two-way table. Construct and interpret a two-way table summarizing data on two categorical variables collected from the same subjects. Use relative frequencies calculated for rows or columns to describe possible association between the two variables. For example, collect data from students in your class on whether or not they have a curfew on school nights and whether or not they have assigned chores at home. Is there evidence that those who have a curfew also tend to have chores?
CCSS8.NS.A.1
Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand informally that every number has a decimal expansion; for rational numbers show that the decimal expansion repeats eventually, and convert a decimal expansion which repeats eventually into a rational number.
CCSS8.NS.A.2
Use rational approximations of irrational numbers to compare the size of irrational numbers, locate them approximately on a number line diagram, and estimate the value of expressions (e.g., π²). For example, by truncating the decimal expansion of √2, show that √2 is between 1 and 2, then between 1.4 and 1.5, and explain how to continue on to get better approximations.