Math Presentations for Google Slides™ 3rd Grade Module 1

What educators are saying
Also included in
- Teach Eureka Math easily using Google Slides™! THIS PRODUCT INCLUDES ALL LESSONS FOR THE YEAR FOR MODULES 1-7.*** VISIT THE INDIVIDUAL LESSONS IN MY STORE FOR COMPLETE PREVIEWS (EACH PREVIEW SHOWS EVERY PAGE IN THE PRODUCT) ***Teach Engage NY Math easily using Google Slides™! These presentations incPrice $99.00Original Price $152.00Save $53.00
Description
THIS PRODUCT INCLUDES ALL LESSONS FOR MODULE 1.
Teach Engage NY Math easily using Google Slides™!
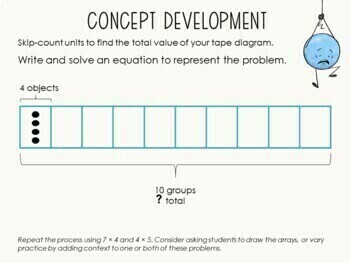
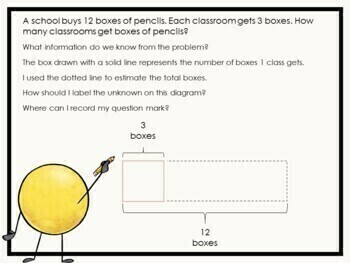
These presentations include slides for each component of the lesson including: Fluency, Application Problem, Concept Development and Student Debrief.
Teaching Engage NY Math using these presentations will:
- Reduce prep time and improves lesson pacing as you don’t have to refer back to the teacher’s manual during the lesson.
- Let anyone follow along. Now, you can feel comfortable leaving the Engage NY Math lesson for substitutes to teach.
- Keep the lesson on track - both you and the students have a visual reminder of what is coming up next in the lesson.
- Help you recover when the lesson goes “off course”.
Adorable “Dot Dudes” theme keeps students engaged throughout the lesson.
Unabridged lessons allow you to teach the curriculum with fidelity.
Editable text gives you the opportunity to customize lessons for your classroom. To secure the clip art I use in my products, the slide backgrounds are not editable.
This product aligns with Engage NY Math, a free program. I am selling my time and creativity in designing supplemental (and engaging) presentations specifically for Google Slides™.