Introduction to Algebraic & Geometric Sequences WebQuest
- PDF
- Webquests
Description
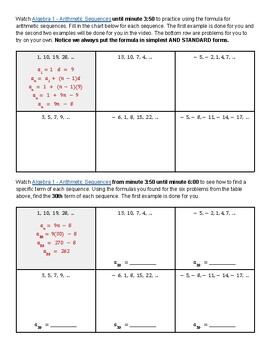
This WebQuest introduces students to sequences by having them watch a video. They learn what a sequence is, how to tell if a sequence is arithmetic or geometric, and how to find the common difference (arithmetic) or common ratio (geometric). In this part of the webquest students get practice problems where they have to identify the type of sequence and find the common difference or common ratio. The second part of this webquest has students watch a video to learn how to write an equation for an arithmetic sequence. They learn the general formula, practice writing the equation for an arithmetic sequence in simplest form and use that formula to find the 30th term in an arithmetic sequence. The third part of this webquest has students watch a video to learn how to write an equation for a geometric sequence. They learn the general formula, practice writing the equation for a geometric sequence and use that formula to find the 8th term in a geometric sequence. The final part of this webquest gives students 8 sequences and asks them to write the equation for each sequence. Note: This webquest does NOT address the recursive formula for either type of sequence.
A link to a digital copy of the assignment only has been added after the answer key to allow for teachers to assign to students digitally.