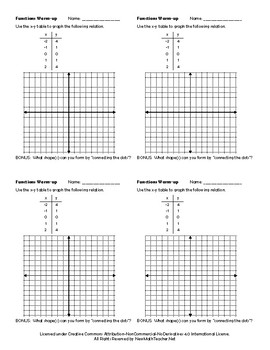
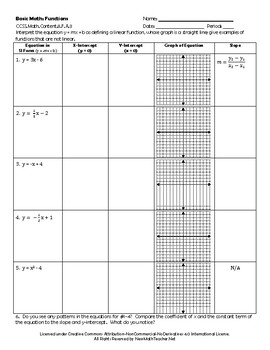
Graphing Linear Functions in Slope Intercept Form
- PDF
Also included in
- Visualize the number system, linear functions, and geometric shapes with student-friendly graphic organizers, number lines, concept mapping, and paper constructions. The perfect packet for busy teachers and inquisitive students! This bundle is standards-based and designed specifically for the 8thPrice $45.00Original Price $48.45Save $3.45
Description
Students will interpret the equation y = mx + b as defining a linear function, whose graph is a straight line. They will also work with examples of functions that are not linear.
Provide feedback and get TPT credit on future purchases:
***Go to your My Purchases page. Click on the Provide Feedback button beside each purchase. You will be taken to a page where you can give a quick rating and leave a short comment for the product. By giving feedback, you gain TPT feedback credits that lower the cost of future purchases. Thank you for your feedback!
Follow me to hear about new discounts, freebies and product launches:
***Click on the green star next to my store logo to become a follower. Thanks for following!
Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.