Grade 5: Math: Whole Year Concept Instructional Video Bundle
- Zip
Products in this Bundle (22)
showing 1-5 of 22 products
Description
Ready for the Bell math resources provide a comprehensive set of print, multimedia resources, and assessments with a real world learning explorations.
A Concept Instructional Video is a combination of a PowerPoint slide deck with teacher notes for you or your parents to present PLUS a video with audio explaining the concept. These mini-lessons break a concept down into more detail and provide the students with a variety of learning strategies to use as they work to understand and be able to apply the concept in real life. Concept Instructional Videos can be used in three ways:
• To teach a concept that comes from a previous grade curriculum and is needed for the Lesson in the present grade curriculum
• To reinforce a concept that was taught in the present grade curriculum but where more practice or a different approach may be useful
•To extend a concept beyond the present grade curriculum
Students view the Concept Instructional Video as a start stop video.
Teachers receive PPT and Google Slide versions of the Concept Instructional Video complete with speaking notes.
This Concept Instructional Video includes:
- 22 Concept Instructional Video
- 22 Concept Instructional Video Powerpoints
- 22 Concept Instructional Video Notes
This Concept Instructional Video is part of the Math 5 lesson bundles. Click below to see these bundles.
Unit Packet: Operations with Whole Numbers
Unit Packet: Patterns and the Coordinate Plane
Unit Packet: Shapes and Volume
Common Core Alignment
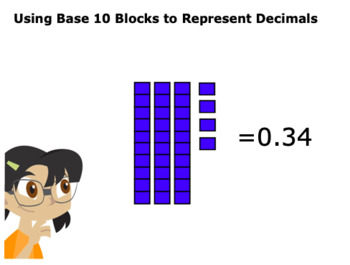
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.5.NBT.A.3.A Read and write decimals to thousandths using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form, e.g., 347.392 = 3 × 100 + 4 × 10 + 7 × 1 + 3 × (1/10) + 9 × (1/100) + 2 × (1/1000).
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.5.NBT.A.3.B Compare two decimals to thousandths based on meanings of the digits in each place, using >, =, and < symbols to record the results of comparisons.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.5.NBT.A.4 Use place value understanding to round decimals to any place.
Add, subtract, multiply, and divide decimals to hundredths, using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction; relate the strategy to a written method and explain the reasoning used.
Generate two numerical patterns using two given rules. Identify apparent relationships between corresponding terms. Form ordered pairs consisting of corresponding terms from the two patterns, and graph the ordered pairs on a coordinate plane. For example, given the rule "Add 3" and the starting number 0, and given the rule "Add 6" and the starting number 0, generate terms in the resulting sequences, and observe that the terms in one sequence are twice the corresponding terms in the other sequence. Explain informally why this is so.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.5.G.A.1 Use a pair of perpendicular number lines, called axes, to define a coordinate system, with the intersection of the lines (the origin) arranged to coincide with the 0 on each line and a given point in the plane located by using an ordered pair of numbers, called its coordinates. Understand that the first number indicates how far to travel from the origin in the direction of one axis, and the second number indicates how far to travel in the direction of the second axis, with the convention that the names of the two axes and the coordinates correspond (e.g., x-axis and x-coordinate, y-axis and y-coordinate).
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.5.G.A.2 Represent real world and mathematical problems by graphing points in the first quadrant of the coordinate plane, and interpret coordinate values of points in the context of the situation.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.5.MD.C.3 Recognize volume as an attribute of solid figures and understand concepts of volume measurement.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.5.MD.C.3.A A cube with side length 1 unit, called a "unit cube," is said to have "one cubic unit" of volume, and can be used to measure volume.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.5.MD.C.3.B A solid figure which can be packed without gaps or overlaps using n unit cubes is said to have a volume of n cubic units.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.5.MD.C.4 Measure volumes by counting unit cubes, using cubic cm, cubic in, cubic ft, and improvised units.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.5.G.B.3 Understand that attributes belonging to a category of two-dimensional figures also belong to all subcategories of that category. For example, all rectangles have four right angles and squares are rectangles, so all squares have four right angles.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.5.G.B.4 Classify two-dimensional figures in a hierarchy based on properties.