Full Year (7-12) Science Vocabulary - Includes 9 Units! (MS / HS)
- Zip
Products in this Bundle (9)
showing 1-5 of 9 products
Description
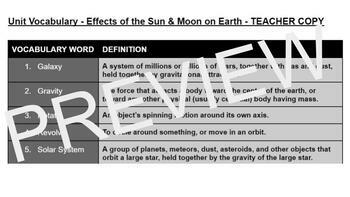
9 Units of Science Vocabulary words with definitions that meet & exceed Common Core and Next Generation Science Standards - rigorously developed over 5 years to match state testing and CCSS & NGSS standards. Bundle contains over 200 vocab words with definitions!
Each Unit contains 25 unique vocabulary words with definitions that match and exceed standards and create a pathway for students to build understanding of science content. How you use these vocabulary words in your classroom is completely up to you. Incorporate them into lessons, or assign them as homework using ourFREE Vocabulary Homework Tracking Sheet</a>.
Pair the vocabulary words with ourVocabulary BINGO sheet</a> for an easy activity to get students excited about identifying words!
Each word was researched and given a definition sourced from a minimum of two trusted locations. Sources include: NASA, Encyclopedia Britannica, Dictionary.com, National Geographic, and more