Eureka Math (Engage NY) Module 5 Topic E PowerPoint Slides
- Zip
What educators are saying
Description
These fun and engaging slides will help you keep your head out of the manual to interact with your students. They are great for visual learners and go along with the Eureka (Engage NY) lessons.
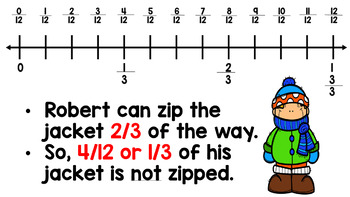
These PowerPoints include every lesson in Module 5 Topic E (Lessons 20-27). Included are the teacher dialog, examples and solutions, I Can Statements, debriefs, and vocabulary.
Our goal is to keep math engaging for the student and teacher. This resource will change the way you teach math! Please provide feedback. We would love to hear from you.
We did not write this curriculum but created these PowerPoint slides to correlate with and supplement Eureka Math (Engage NY). Eureka Math (Engage NY) is a free curriculum that can be found at GreatMinds.org or www.engageny.org.