Conditional Probability and Two-Way Worksheet, CW, HW, Review CP Stats, Ap Stats
- PDF
Description
If you are looking for an easy to follow for students. You are at the right place. This is a quick and easy to follow activity sheet that brings across the concept clear and precise. Teachers in my department love this activity sheet. This is useful of CP Probability and Statistics, AP Statistics and Algebra 1 statistics unit.
Probability and Conditional Probability Objectives
At the end of the lesson students should be able to:
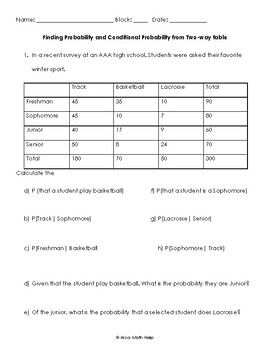
1. Interpret two-way tables
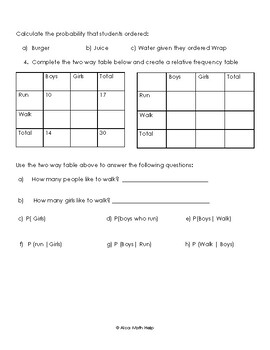
2. Create relative frequency tables for whole tables
3. Define probability and conditional probability
4. Differentiate the difference between probability and conditional probability
5. Identify marginal frequencies and sample space
6. Examine the association between categorical variables
7. Describe patterns that exist
8. Prove independence among categorical variables
9. Write conditional probability statement and summarize them
10. Use probability and conditional probability formulas to solve related questions