Math Class Rocks
1.2k Followers
Grade Levels
6th - 8th, Homeschool
Subjects
Resource Type
Standards
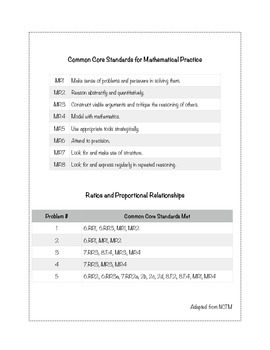
CCSS6.RP.A.1
CCSS6.RP.A.3
CCSS7.RP.A.3
CCSS8.F.B.4
CCSSMP1
Formats Included
- Zip
Pages
8 pages
Math Class Rocks
1.2k Followers
Description
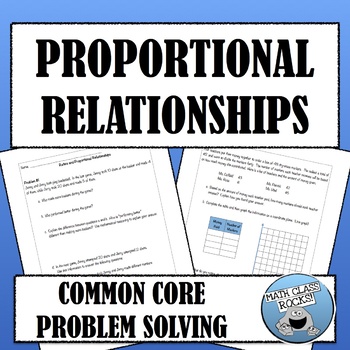
Have you been desperately trying to align your middle school math curriculum to the common core? If so, this problem solving set is for you (and your students, of course!) This set contains 3 higher level, multi-step problems* specifically aligned to the common core for grades 6-8. These problems focus on Proportional Relationships. The first problem is very basic, but the rigor increases as students move through the problem set.
*There are two additional problems in this set, but due to limits on posting "free" items, I could not upload the entire set!
Inspired by resources endorsed by the NCTM, I think this will be a valuable addition to your curriculum.
Common Core Standards for math concepts as well as mathematical practices are provided and answer keys are also included.
This is my VERY FIRST product on TPT, so please let me know if you like what I've done and I will gladly upload more of the materials I've created. Thank you SO much!!
*There are two additional problems in this set, but due to limits on posting "free" items, I could not upload the entire set!
Inspired by resources endorsed by the NCTM, I think this will be a valuable addition to your curriculum.
Common Core Standards for math concepts as well as mathematical practices are provided and answer keys are also included.
This is my VERY FIRST product on TPT, so please let me know if you like what I've done and I will gladly upload more of the materials I've created. Thank you SO much!!
Total Pages
8 pages
Answer Key
Included
Teaching Duration
1 hour
Report this resource to TPT
Reported resources will be reviewed by our team. Report this resource to let us know if this resource violates TPT’s content guidelines.
Standards
to see state-specific standards (only available in the US).
CCSS6.RP.A.1
Understand the concept of a ratio and use ratio language to describe a ratio relationship between two quantities. For example, “The ratio of wings to beaks in the bird house at the zoo was 2:1, because for every 2 wings there was 1 beak.” “For every vote candidate A received, candidate C received nearly three votes.”
CCSS6.RP.A.3
Use ratio and rate reasoning to solve real-world and mathematical problems, e.g., by reasoning about tables of equivalent ratios, tape diagrams, double number line diagrams, or equations.
CCSS7.RP.A.3
Use proportional relationships to solve multistep ratio and percent problems. Examples: simple interest, tax, markups and markdowns, gratuities and commissions, fees, percent increase and decrease, percent error.
CCSS8.F.B.4
Construct a function to model a linear relationship between two quantities. Determine the rate of change and initial value of the function from a description of a relationship or from two (𝘹, 𝘺) values, including reading these from a table or from a graph. Interpret the rate of change and initial value of a linear function in terms of the situation it models, and in terms of its graph or a table of values.
CCSSMP1
Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. Mathematically proficient students start by explaining to themselves the meaning of a problem and looking for entry points to its solution. They analyze givens, constraints, relationships, and goals. They make conjectures about the form and meaning of the solution and plan a solution pathway rather than simply jumping into a solution attempt. They consider analogous problems, and try special cases and simpler forms of the original problem in order to gain insight into its solution. They monitor and evaluate their progress and change course if necessary. Older students might, depending on the context of the problem, transform algebraic expressions or change the viewing window on their graphing calculator to get the information they need. Mathematically proficient students can explain correspondences between equations, verbal descriptions, tables, and graphs or draw diagrams of important features and relationships, graph data, and search for regularity or trends. Younger students might rely on using concrete objects or pictures to help conceptualize and solve a problem. Mathematically proficient students check their answers to problems using a different method, and they continually ask themselves, "Does this make sense?" They can understand the approaches of others to solving complex problems and identify correspondences between different approaches.