BIG BUNDLE Genetic Disorders and DNA Mutations with Chromosomal Abnormalities
- Zip
Products in this Bundle (5)
Also included in
- The "Mega Genetics / DNA / Chromosomes Bundle" starts your students going over DNA and RNA with powerpoints and differentiated guided notes. You have a set of "DNA Processes" Word Wall Coloring sheets to help students become familiar with the vocabulary words for the "DNA Processes" lesson. The "DNAPrice $59.99Original Price $89.50Save $29.51
Description
BIG BUNDLE Genetic Disorders and DNA Mutations with Chromosomal Abnormalities is an excellent resource to use in a traditional, hybrid, or distance learning environment. The student-guided notes and worksheets are in both printable and digital fillable pdf files. The digital fillable pdf files are great for online platforms such as Google Classroom, Schoology, or others. The fillable pdf forms can be filled out using Adobe Acrobat, Lumen, Kami, or other free pdf-editing applications.
The Genetic Disorders Bundle goes over the DNA mutations and couples each of them with a disease that people are affected by. The causes of genetic mutations, deletion, inversion, insertion, and duplication, are explained with simple diagrams. Point mutation frameshift mutation, chromosomal mutations, and sex-linked mutations are also included with accompanying diseases such as sickle cell anemia, PKU, Huntington's, and Down's Syndrome. The end of the PowerPoint presentation introduces the students to human genetic mutations with beneficial side effects.
The guided notes come in two formats a worksheet style and a mini-book style. Both as easy to implement and have a student form and modified fill-in-the-blank form for students with an IEP or handwriting challenges. The fill-in-the-blank style also comes in handy when experiencing a time crunch. there are student prompts throughout the notes and both formats end with a page of review questions.
There are writing task cards and three sets of problem sets. The writing prompts give students an opportunity to answer questions by creating small paragraphs while using genetic vocabulary. In the Single-Strand DNA Mutation set, the students will model DNA mutations in single DNA strands. Students will model deletion, point, insertion, inversion, and duplication mutations. They will analyze how the mutations change the amino acid sequence in the polypeptide chains.
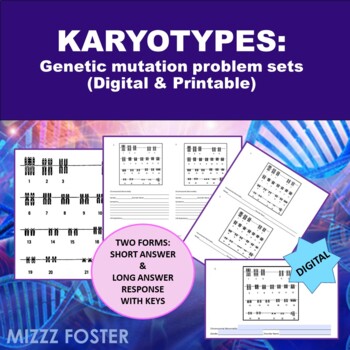
The last two sets center around karyotype analysis. Students will diagnose trisomy, monosomy, translocation, or partial deletion chromosome mutations along with the person's gender. Students will use the internet to research the common names of the mutations, symptoms, and life expectancy and the long answer form also has a place for students to write the symptoms of the genetic disorders.
This bundle includes:
Genetic Disorders: Mistakes in the DNA code, DNA mutations PowerPoint
Genetic Disorders: Mistakes in the DNA code, DNA mutations Worksheets w/t Key
Genetic Mutations: DNA Mutations Writing Task Cards Secondary Science
Mutations in DNA: Single strand DNA mutations Problem Set
Genetic Disorders / Mutations: Karyotype Problem Sets Worksheets
GREAT FOR ANY STATE!
Texas Biology TEKS
(6) Science concepts. The student knows the mechanisms of genetics, including the role of nucleic acids and the principles of Mendelian Genetics. The student is expected to:
(A) identify components of DNA, and describe how information for specifying the traits of an organism is carried in the DNA;
(B) recognize that components that make up the genetic code are common to all organisms;
(C) explain the purpose and process of transcription and translation using models of DNA and RNA;
(D) recognize that gene expression is a regulated process;
(E) identify and illustrate changes in DNA and evaluate the significance of these changes;
(F) predict possible outcomes of various genetic combinations such as monohybrid crosses, dihybrid crosses and non-Mendelian inheritance;
(G) recognize the significance of meiosis to sexual reproduction; and
(H) describe how techniques such as DNA fingerprinting, genetic modifications, and chromosomal analysis are used to study the genomes of organisms.
(7) Science concepts. The student knows evolutionary theory is a scientific explanation for the unity and diversity of life. The student is expected to:
(F) analyze and evaluate the effects of other evolutionary mechanisms, including genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and recombination; and
NEW GENERATION SCIENCE STANDARDS
HS-LS4-2. Construct an explanation based on evidence that the process of evolution primarily results from four factors: (1) the potential for a species to increase in number, (2) the heritable genetic variation of individuals in a species due to mutation and sexual reproduction, (3) competition for limited resources, and (4) the proliferation of those organisms that are better able to survive and reproduce in the environment. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on using evidence to explain the influence each of the four factors has on number of organisms, behaviors, morphology, or physiology in terms of ability to compete for limited resources and subsequent survival of individuals and adaptation of species. Examples of evidence could include mathematical models such as simple distribution graphs and proportional reasoning.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include other mechanisms of evolution, such as genetic drift, gene flow through migration, and co-evolution.]
MS-LS3-1. Develop and use a model to describe why structural changes to genes (mutations) located on chromosomes may affect proteins and may result in harmful, beneficial, or neutral effects to the structure and function of the organism. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on conceptual understanding that changes in genetic material may result in making different proteins.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include specific changes at the molecular level, mechanisms for protein synthesis, or specific types of mutations.]