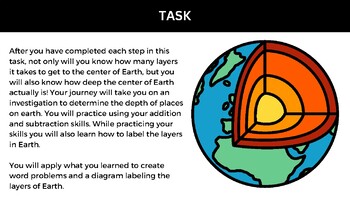
Adding and Subtracting Whole Numbers by exploring the layers of Earth Webquest
Michele McKie
28 Followers
Grade Levels
3rd - 6th
Subjects
Resource Type
Standards
CCSS3.NBT.A.2
CCSS4.NBT.B.4
CCSSMP4
NGSS4-ESS2-2
Formats Included
- PDF
- Webquests
Pages
26 pages
Michele McKie
28 Followers
Compatible with Digital Devices
The Teacher-Author has indicated that this resource can be used for device-based learning.
Description
Student Learning Objectives:
- Practice using whole digit addition and subtraction using expanded form models
- Locate depths of places on earth
- Identify the layers of the earth
- Create word problems using addition & subtraction
This activity is intended to be used as a supplemental to instruction after students have practiced using the expanded method for addition and subtraction of whole numbers. Students will go through an inquiry based method to identify depths of various places on Earth. Students will learn about the layers of the earth through reading and video introductions. Students will use their inquiry to create addition and subtraction word problems using what they learned through out the process.
Total Pages
26 pages
Answer Key
Rubric only
Teaching Duration
90 minutes
Report this resource to TPT
Reported resources will be reviewed by our team. Report this resource to let us know if this resource violates TPT’s content guidelines.
Standards
to see state-specific standards (only available in the US).
CCSS3.NBT.A.2
Fluently add and subtract within 1000 using strategies and algorithms based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction.
CCSS4.NBT.B.4
Fluently add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm.
CCSSMP4
Model with mathematics. Mathematically proficient students can apply the mathematics they know to solve problems arising in everyday life, society, and the workplace. In early grades, this might be as simple as writing an addition equation to describe a situation. In middle grades, a student might apply proportional reasoning to plan a school event or analyze a problem in the community. By high school, a student might use geometry to solve a design problem or use a function to describe how one quantity of interest depends on another. Mathematically proficient students who can apply what they know are comfortable making assumptions and approximations to simplify a complicated situation, realizing that these may need revision later. They are able to identify important quantities in a practical situation and map their relationships using such tools as diagrams, two-way tables, graphs, flowcharts and formulas. They can analyze those relationships mathematically to draw conclusions. They routinely interpret their mathematical results in the context of the situation and reflect on whether the results make sense, possibly improving the model if it has not served its purpose.
NGSS4-ESS2-2
Analyze and interpret data from maps to describe patterns of Earth’s features. Maps can include topographic maps of Earth’s land and ocean floor, as well as maps of the locations of mountains, continental boundaries, volcanoes, and earthquakes.