Adding and Subtracting Radical Expressions Printable
Description
Do you NOT have time to create your own handouts, worksheets, or homework assignments? We have you covered!
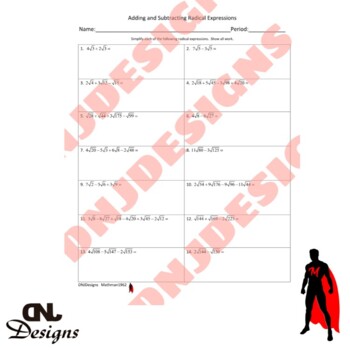
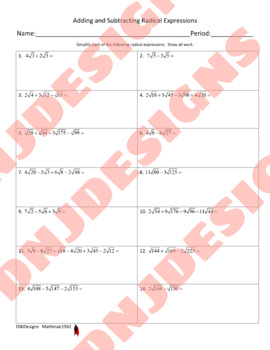
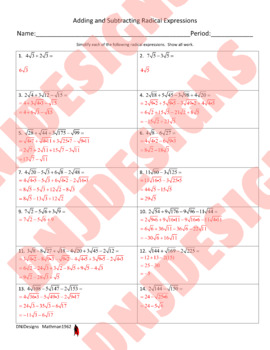
This activity covers adding and subtracting radical expressions. All radicals are square roots and most require simplifying the radical before adding or subtracting like terms in the expression. There are fourteen problems that range from one step to multiple steps in order to simplify completely. This activity can be used as guided practice in class or as a homework assignment.
This activity can also act as a differentiated instruction activity for those students that need additional practice or remediation in this topic. It can also be used as enrichment for students that need to be challenged with a topic beyond what they are currently learning.
Check out all of our stores and sites
DNJDesigns Creative Fabrica Store
Mathman1962 YouTube Channel - free math tutorial videos
Check all of our websites for FREEBIES (free printables, clipart, interactive content, and more!