Multiplication & Division: Project Based Learning Activity
Christy Howe
2.8k Followers
Grade Levels
3rd - 4th, Homeschool
Subjects
Resource Type
Standards
CCSS3.OA.A.1
CCSS3.OA.A.2
CCSS3.OA.A.3
CCSS3.OA.A.4
CCSS3.OA.B.5
Formats Included
- PDF
Pages
13 pages
Christy Howe
2.8k Followers
What educators are saying
My students enjoyed making board games for others to play. Great resource for early finishers or as an enrichment activity.
Fantastic resource! So easy and engaging! My students look forward to using it! Definitely recommend!
Description
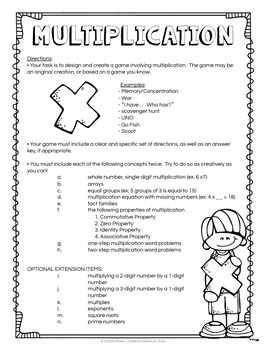
In this Project Based Learning activity, students create one or more games to develop and extend their understanding of multiplication and division. The project encourages student creativity, while also providing guidelines to ensure student accountability of learning and standards. Once students have created their games, I often use them in centers & stations, as Anchor Activities, Parent Involvement, and for ongoing practice and remediation (as needed).
This download includes:
• an activity page for multiplication
• an activity page for division
• an activity page combining multiplication and division
• an analytic rubric with detailed descriptors (can be used with all three PBL activities)
• a student checklist with places for peer evaluation and teacher review. (can be used with all three PBL activities)
• Teacher Tips for implementation
Activities in this hands-on project actively meet the following Common Core State Standards:Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division:
• 3.OA.A.1
• 3.OA.A.2
• 3.OA.A.3
• 3.OA.A.4
Understand properties of multiplication and the relationship between multiplication and division:
• 3.OA.B.5
• 3.OA.B.6
• 3.OA.C.7
***************************************************************************
If you and your students enjoy these activities, you may also like the following differentiated enrichment activities:
• THINK! Math Enrichment Activities.
• Brain Food! The Original.
• Fraction Pattern Block Puzzles.
***************************************************************************
Please contact me if you have any questions! I want you to be 1,000% happy with your purchase!
Christy
© Christy Howe 2014. Materials are intended for personal use in one classroom only. For use in multiple classrooms, please purchase additional licenses.
This download includes:
• an activity page for multiplication
• an activity page for division
• an activity page combining multiplication and division
• an analytic rubric with detailed descriptors (can be used with all three PBL activities)
• a student checklist with places for peer evaluation and teacher review. (can be used with all three PBL activities)
• Teacher Tips for implementation
Activities in this hands-on project actively meet the following Common Core State Standards:Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division:
• 3.OA.A.1
• 3.OA.A.2
• 3.OA.A.3
• 3.OA.A.4
Understand properties of multiplication and the relationship between multiplication and division:
• 3.OA.B.5
• 3.OA.B.6
• 3.OA.C.7
***************************************************************************
If you and your students enjoy these activities, you may also like the following differentiated enrichment activities:
• THINK! Math Enrichment Activities.
• Brain Food! The Original.
• Fraction Pattern Block Puzzles.
***************************************************************************
Please contact me if you have any questions! I want you to be 1,000% happy with your purchase!
Christy
© Christy Howe 2014. Materials are intended for personal use in one classroom only. For use in multiple classrooms, please purchase additional licenses.
Total Pages
13 pages
Answer Key
Rubric only
Teaching Duration
N/A
Report this resource to TPT
Reported resources will be reviewed by our team. Report this resource to let us know if this resource violates TPT’s content guidelines.
Standards
to see state-specific standards (only available in the US).
CCSS3.OA.A.1
Interpret products of whole numbers, e.g., interpret 5 × 7 as the total number of objects in 5 groups of 7 objects each. For example, describe a context in which a total number of objects can be expressed as 5 × 7.
CCSS3.OA.A.2
Interpret whole-number quotients of whole numbers, e.g., interpret 56 ÷ 8 as the number of objects in each share when 56 objects are partitioned equally into 8 shares, or as a number of shares when 56 objects are partitioned into equal shares of 8 objects each. For example, describe a context in which a number of shares or a number of groups can be expressed as 56 ÷ 8.
CCSS3.OA.A.3
Use multiplication and division within 100 to solve word problems in situations involving equal groups, arrays, and measurement quantities, e.g., by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem.
CCSS3.OA.A.4
Determine the unknown whole number in a multiplication or division equation relating three whole numbers. For example, determine the unknown number that makes the equation true in each of the equations 8 × ? = 48, 5 = __ ÷ 3, 6 × 6 = ?.
CCSS3.OA.B.5
Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide. Examples: If 6 × 4 = 24 is known, then 4 × 6 = 24 is also known. (Commutative property of multiplication.) 3 × 5 × 2 can be found by 3 × 5 = 15, then 15 × 2 = 30, or by 5 × 2 = 10, then 3 × 10 = 30. (Associative property of multiplication.) Knowing that 8 × 5 = 40 and 8 × 2 = 16, one can find 8 × 7 as 8 × (5 + 2) = (8 × 5) + (8 × 2) = 40 + 16 = 56. (Distributive property.)