Math Facts Self-Checking Google Sheets Activity [Whole, Rational, Integers]
- Google Sheets™
- Excel Spreadsheets

Description
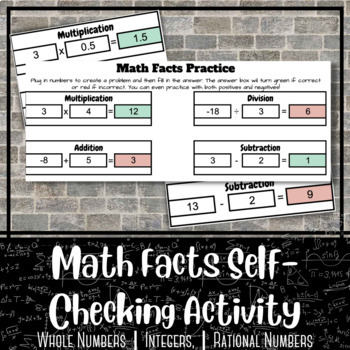
Student-generated and self-checking assignments are a great way to engage students thinking in a new way.
With this activity, students will be able to create their own problems by plugging numbers into the given boxes and then solving the problem that they create. The answer box will then turn color based on student response [green = correct and red = incorrect]. This is a great activity as it works for students of all ages. This works with all whole numbers (ex. 1, 2, 3, 4,...), integers (ex. -2, -1, 0, 1, 2,...), and rational numbers (ex. 0.75, 1.5, 3.4,...).
This activity works great as an early finisher activity or a math center destination to review or preview these essential math skills.
This activity includes:
- Google Sheets Document with
- Multiplication Self-Checking Program
- Division Self-Checking Program
- Addition Self-Checking Program
- Subtraction Self-Checking Program
***After purchase, please be sure to leave a review to not only receive TPT credit for yourself but also help to improve resources for the future!***