Key Features of Linear Functions Notes | Graphing Linear Equations
Lauren Fulton
5.8k Followers
Resource Type
Standards
CCSS8.EE.B.6
CCSS8.F.A.3
CCSSHSF-LE.A.2
Formats Included
- PDF
Pages
2+ Teacher Keys
Lauren Fulton
5.8k Followers
What educators are saying
Use this in our notebooks as an added visual for notes on linear functions. Students were able to add color and personalize it.
Description
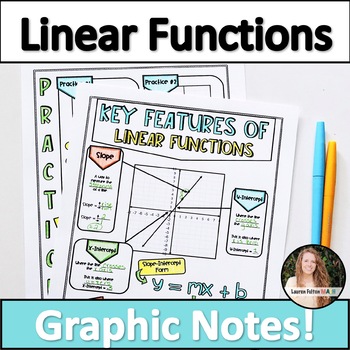
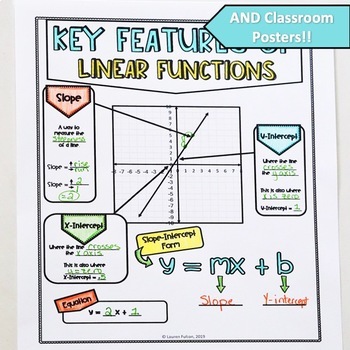
Looking for an engaging way to teach key features of linear functions in slope-intercept form? These graphic notes are perfect for student engagement and can double as classroom posters!
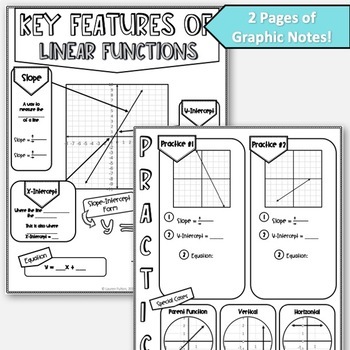
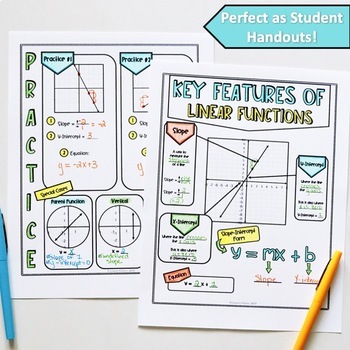
These content rich, beautiful notes serve as a great introduction to your unit and work wonderfully as a quick-reference for students. Material Covered: Slope from graphs, y-intercept, x-intercept, slope-intercept form, horizontal lines, parent function, and vertical lines.
This Product Includes
- 1 Page of Key Features of Graphs & Slope-Intercept Equation
- 1 Page of Practice & Additional Information
- 2 Pages of Teacher Examples/Completed Notes
Related Products
Total Pages
2+ Teacher Keys
Answer Key
Included
Teaching Duration
40 minutes
Report this resource to TPT
Reported resources will be reviewed by our team. Report this resource to let us know if this resource violates TPT’s content guidelines.
Standards
to see state-specific standards (only available in the US).
CCSS8.EE.B.6
Use similar triangles to explain why the slope m is the same between any two distinct points on a non-vertical line in the coordinate plane; derive the equation 𝘺 = 𝘮𝘹 for a line through the origin and the equation 𝘺 = 𝘮𝘹 + 𝘣 for a line intercepting the vertical axis at 𝘣.
CCSS8.F.A.3
Interpret the equation 𝘺 = 𝘮𝘹 + 𝘣 as defining a linear function, whose graph is a straight line; give examples of functions that are not linear. For example, the function 𝘈 = 𝑠² giving the area of a square as a function of its side length is not linear because its graph contains the points (1,1), (2,4) and (3,9), which are not on a straight line.
CCSSHSF-LE.A.2
Construct linear and exponential functions, including arithmetic and geometric sequences, given a graph, a description of a relationship, or two input-output pairs (include reading these from a table).