7th Grade Math Statistics and Probability Study Guide or Review
Math Maker
898 Followers
Grade Levels
6th - 7th, Homeschool
Subjects
Resource Type
Standards
CCSS7.SP.A.1
CCSS7.SP.A.2
CCSS7.SP.B.3
CCSS7.SP.B.4
CCSS7.SP.C.5
Formats Included
- PDF
Pages
4 pages
Math Maker
898 Followers
What educators are saying
Thank you for the resource. This really allowed my students to gain a deeper understanding of the skills and show what they had learned and mastery of the topic.
Description
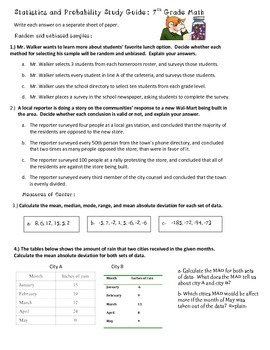
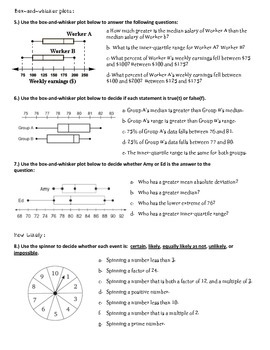
4 page study guide containing over 60 questions aligned to 7th grade SP common core standards. All questions are open-ended. Answer key is provided.
Covers the following topics:
~ Random and unbiased samples
~ Using data from a sample to make predictions about a population
~ Measures of central tendency
~ Range and mean absolute deviation
~ Box-and-whisker plots
~ The likeliness of an even occurring
~ Simple and compound probability
~ Independent and dependent events
~ Probability trees
This study guide is aligned to my unit exam on statistics and probability.
Covers the following topics:
~ Random and unbiased samples
~ Using data from a sample to make predictions about a population
~ Measures of central tendency
~ Range and mean absolute deviation
~ Box-and-whisker plots
~ The likeliness of an even occurring
~ Simple and compound probability
~ Independent and dependent events
~ Probability trees
This study guide is aligned to my unit exam on statistics and probability.
Total Pages
4 pages
Answer Key
Included
Teaching Duration
90 minutes
Last updated Jan 14th, 2015
Report this resource to TPT
Reported resources will be reviewed by our team. Report this resource to let us know if this resource violates TPT’s content guidelines.
Standards
to see state-specific standards (only available in the US).
CCSS7.SP.A.1
Understand that statistics can be used to gain information about a population by examining a sample of the population; generalizations about a population from a sample are valid only if the sample is representative of that population. Understand that random sampling tends to produce representative samples and support valid inferences.
CCSS7.SP.A.2
Use data from a random sample to draw inferences about a population with an unknown characteristic of interest. Generate multiple samples (or simulated samples) of the same size to gauge the variation in estimates or predictions. For example, estimate the mean word length in a book by randomly sampling words from the book; predict the winner of a school election based on randomly sampled survey data. Gauge how far off the estimate or prediction might be.
CCSS7.SP.B.3
Informally assess the degree of visual overlap of two numerical data distributions with similar variabilities, measuring the difference between the centers by expressing it as a multiple of a measure of variability. For example, the mean height of players on the basketball team is 10 cm greater than the mean height of players on the soccer team, about twice the variability (mean absolute deviation) on either team; on a dot plot, the separation between the two distributions of heights is noticeable.
CCSS7.SP.B.4
Use measures of center and measures of variability for numerical data from random samples to draw informal comparative inferences about two populations. For example, decide whether the words in a chapter of a seventh-grade science book are generally longer than the words in a chapter of a fourth-grade science book.
CCSS7.SP.C.5
Understand that the probability of a chance event is a number between 0 and 1 that expresses the likelihood of the event occurring. Larger numbers indicate greater likelihood. A probability near 0 indicates an unlikely event, a probability around 1/2 indicates an event that is neither unlikely nor likely, and a probability near 1 indicates a likely event.